Production Design & Control
Company
Background
Case Background
The demand
for the jam and bottled fruit of GSH Conserves is growing rapidly. After moving
the kitchen to a larger factory, Joey Gan still found that the company is
facing the challenges brought by bottlenecks, that limited their production
quantity. They are only able to fulfill the order without any safety stock. Moreover,
workers and machine were often unoccupied. A new smooth production plan is
needed immediately so that Joey can maximize his production quantity and
resource efficiency.
Class Exercises
Q1.
In the situation of 100 kg demand of jam with batch size of 5 kg, the bottleneck is the process of boiling and adding sugar to jam, with the capacity of 111.1 kg per day, given that the utilization is 90%. Although some of the resources’ utilization is low, such as scraping skins and blending dragon fruit and lychees, which may let workers and machines sitting idle, the demand is fulfilled, no improvement to make in this situation.
Q2.
In the situation of 100 kg demand of jam with batch size of 10 kg, the bottleneck has remained unchanged, but with a larger capacity of 127.1 kg per day, given that the utilization is 78%. Some of the resources’ utilization is lower after the change of batch size, such as washing and peeling and blending dragon fruit and lychees. In this situation, the demand is fulfilled, no improvement to make.
Q3.
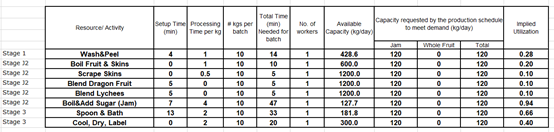
In the situation of 100 kg demand of jam with batch size of 5 kg, as the bottleneck is the process of boiling and adding sugar to jam, the maximum demand per day will be its capacity, which is 111.1 kg per day.
The chart
shows the relation between batch size and utilization rate at the process of boiling
and adding sugar to jam. From the chart, we can conclude that the best option
of batch size is 20 kg, as the impact of lowering the utilization rate by increasing
the batch size is keep decreasing.
Q4.
In the situation of 120 kg demand of jam with batch size of 5 kg, as the bottleneck is still the process of boiling and adding sugar to jam, with the capacity of 111.1 kg per day, given that the utilization is 108%. This means there is insufficient production quantity (shortage of 9 kg jam) to fulfill the demand, the worker who is responsible for boiling and adding sugar to jam has to work overtime. By increasing the batch size, we can make an improvement on the utilization rate. Hiring additional workers is also a feasible way to deal with.
The utilization rate of boiling and adding sugar to jam dropped to 94% and the capacity increased to 127.7 kg per day after increasing the batch size from 5 kg to 10 kg. The company is now able to fulfill the demand within regular working hours.
Q5.
In the situation of 120 kg demand of jam and bottle fruit with batch size of 5 kg, the bottleneck is the process of spooning and bathing, with the capacity of 181.8 kg per day, given that the utilization is 132%. Demand is not fulfilled, and workers needed to work overtime.
Q6.
By adding one more worker in the process of spooning and bathing, the utilization rate dropped from 132% to 66%, as the worker double the productivity of the process. The bottleneck is now move back to the process of boiling and adding sugar to jam, with a utilization rate of 108%.
ICE
Question
Redesign the Process
Above is our new production flow plan. Stage 1 is the process of washing and peeling for both jam and fruit. Then it will be dived into two different stages, stage J and F. Stage J included the process from boiling fruit and skins to boiling and adding sugar to jam. Stage F included cutting dragon fruit to boiling and adding sugar to the fruit. After finishing stage J and F respectively, both jam and fruit will enter stage 3, which is the spooning, bathing and labeling process.
To find the optimal solution for the production plan, we used the solver
function in excel. Our goal is to
maximize the capacity and lower the implied utilization of each activity as
much as possible. The number of assigned workers is set as changing variable.
For the constraints, the total number of workers cannot be more than 10, and
all variables should be an integer.
After running the solver, we can get the result of 300 kg per day of maximum available capacity.
New Technologies to Improve Production
Apart from the new design of the production plan, using new technologies is also a feasible plan to do so. We suggest using following ways to improve the production process:
1. Automate the process
Incorporate automatic stirrer can be adopted which can stir in a more consistent and auto manner to avoid overcooking and reduce the labor needed for stirring. An AI system can be used to control and track the temperature while boiling and water bath process to control the product quality. Auto drying and labeling machine can help to hasten the last process.
2. Use barcode/ RFID
Instead of manually typing the information to the excel sheet, we suggest to use barcode or RFID chips to record the product data, so to achieve efficiency and save time, especially during peak seasons.
3. Inventory management software
Inventory
management software allows users to set the reorder point for materials
automatically so that materials shortages or occur of wrong manually
calculation of the stock amounts can be avoided.
Ways to Ramp Up Sales
An increasing sales figure is an important element of the growth of the company. Below are the suggestions we made for GSH Conserves to ramp up their sales.
Promotion
As GHS conserves business uses 100% fruit without adding artificial flavoring, additives or preservatives, a certain portion of their target customer would value their health, hence, are eager to buy natural and healthy foods. Therefore, we suggest that GHS conserves can also sell their fruit jam products through healthy food store or online store, such as i-herb. As one of the existing selling channels is through Isetan, it can also set up a promotion booth in that department store, which provide free tasting and directly promote to the customers. Besides, the company can adopt social media marketing. It can set up a Facebook page to promote the jam and bottled fruit at a lower cost. Utilizing social medial can be easier to reach and increase the interaction with potential customers. Also, can better know what their customers need and receive suggestions to improve their products.
Operation
Plan
GHS
conserves made jam by using different tropical fruit, it made their jam stand
out in the market. However, there are many substitutes for jam in the market.
Customers can easily find another brand’s jam. We suggest that GSH can produce
bottled fruit with more tropical fruit flavor because tropical fruit is harder
to preserve which makes the supply in the market scarce. It will help them to
increase sales from selling bottled fruit. GSH conserves also can expand the
market by cooperating with schools or businesses to promote a healthy lifestyle.
For instance, the school can provide bottled fruit to the students during the
lunch hour or as a side note, they can provide bottled fruit or jam for
employees to encourage them to eat healthily in their daily life as employee
health is crucial. By instilling the idea of eating healthily, it can widen the
potential market. As mentioned, the target customer of GSH conserves would emphasize
their health, establishing branches or vending machines near sports facilities, for example gym rooms and sports centers, would be a good way to reach
its target customer.
Reflection
From this
case, we can see a detail production process with different steps and duration.
Through the excel sheet demonstration, we found that the utilization rate can show
a great difference among the process. For example, in Q4, the max utilization rate
is 108% while the min is 10%. It is interesting to imagine that a worker is
working so hard to meet the target while another one is just working an hour a
day and playing with their smartphone in the rest of the workday. But this
example also shows us the impact of bottleneck to production efficiency can
be great, which deepens our understanding and memory. Other than that, this
example also tells us that not only the increase of recourse can lower the utilization
rate, but the increase of batch size can have the same effect on the utilization
rate as more material shares the duration.
References
Chubby Hubby. (2014, June 16). An Interview With Joey Gan of GSH Conserves, A Boutique Singaporean Food Producer. Retrieved from http://chubbyhubby.net/recipes/interview-joey-gan-gsh-conserves-boutique-singaporean-food-producer/
Foodmiles. (n.d.). Food Miles Calculator. Retrieved from https://www.foodmiles.com/
The General Co. (2014, February 5). The Story Of Joey Gan, founder of GSH Conserves. Retrieved from https://thegeneralco.sg/blogs/general-journal/joey-gan-founder-of-gsh-conserve
Vulcanpost. (2015, August 26). GSH Conserves: How A Tree Doctor Stumbled Onto The Path Of Jam Making. Retrieved from https://vulcanpost.com/352421/gsh-conserves-tree-doctor-stumbled-onto-path-jam-making/













.svg.png)

留言
發佈留言